Introduction

The advent of the Internet in the 1990s has fueled the emergence and rapid growth of gay communities across Asia. Broadband Internet access in many countries in the region has allowed MSM to meet and communicate with one another, overcoming barriers such as social stigma and government regulation.
In the last few years, there have been reports of new or newly identified epidemics of HIV among men who have sex with men (MSM) in Asia[i], against a backdrop of a global epidemic of HIV infection where MSM continue to be disproportionately affected. Some studies suggest a strong correlation between Internet use and multiple risk behaviours of MSM[ii], which may be contributing to the epidemic. The Internet may have made it easier to have more sex partners, of seroconcordant or serodiscordant HIV status, and has become one of the most popular venues for MSM to find sex partners. The Internet has also been associated with unprotected sex and sexually transmitted disease outbreaks [iii-ix].
Objectives
To conduct an annual large scale, multi-language Internet-based survey of MSM who use the Internet on their sexual history, risk behaviour, HIV and STI testing history and self-reported HIV prevalence which will allow the direct comparison of similar populations from different countries
Methods
The Asia Internet MSM Sex Survey was conducted over 2 months of each year. Participants were invited to complete a confidential, anonymous self-administered questionnaire online and asked to provide information on socio-demographic characteristics including age, ethnicity, educational attainment, and employment. They were also asked about their sexual orientation and HIV test history. Men were asked about where they met their sexual partners and how old they were when they first had anal sex with another man and whether a condom was used during their first anal sex experience. There was no incentive offered to complete the questionnaire.
The survey was launched in English in 2009 (www.msmsexsurvey.com), and expanded to include 9 additional Asian languages and dialects in 2010 under the new AIMSS branding (www.2010aimss.com): Chinese (Mandarin Simplified, Taiwanese Traditional and Cantonese), Japanese, Thai, Tagalog, Bahasa Malaysia, Bahasa Indonesia and Vietnamese. Participants could seamlessly switch between languages at any point in the survey. Translations were provided by native speakers who were also either MSM from a community-based organisation or researcher working in HIV so as to ensure the language used would be appropriate to local MSM contexts.
The 2010 survey contained new questions on male clients of men who sold sex, alcohol use before or during sex, age of sexual debut and several other new sections.
Participants were recruited exclusively through online methods, primarily through web banners and electronic direct mailers (EDMs) sent through a network of community coalition partners. Over 40 community coalition partners from 12 countries participated in 2010. These partners include gay websites, bars and clubs, saunas and community organisations.
Results
A total of 5,806 completed the online questionnaire in 2009 and 13,882 in 2010.
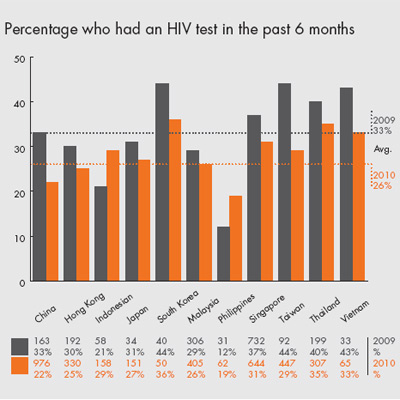
The median age of the men at the time of the survey was 25 years in 2009 vs 29 years in 2010 (range 11 to 77 years). The majority of the men were of Asian ethnicity and most were either in full time employment or education. Over half said they had a University or post-graduate degree. Nearly all the men self-identified as gay or bisexual (97% in 2010 vs 98% in 2009) and about a third said they have been in a relationship with another man for more than 6 months at the time of the survey. 41% in 2010 vs 30% in 2009 of the men have had an HIV test; of those who have had a test, self-reported HIV prevalence was
5% in 2010 vs 6% in 2009.
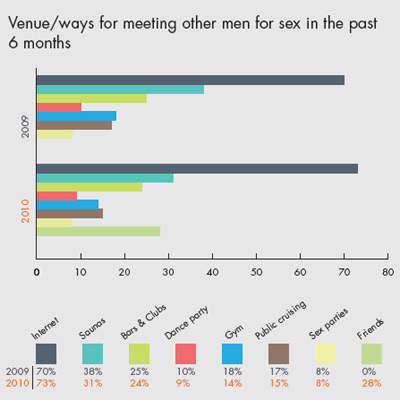
Around 60% of the online sample reported little or no risk for HIV transmission. These men either had no sexual contact, only oral sex (no anal intercourse), or always used a condom for anal intercourse. Over 70% of the participants had used the Internet to seek male sexual partners.
Differences were found in between participants from each country in several areas, highlighting the diversity of the populations.
The following are selected charts from the report. To view references and the report (in PDF) in its entirety, click here to download.
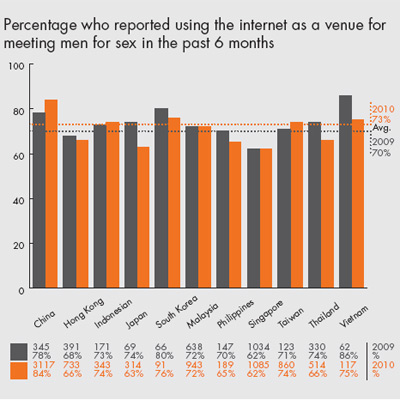
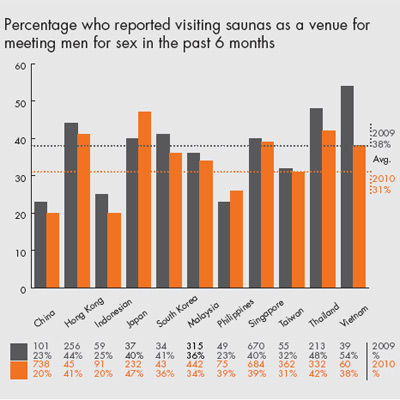
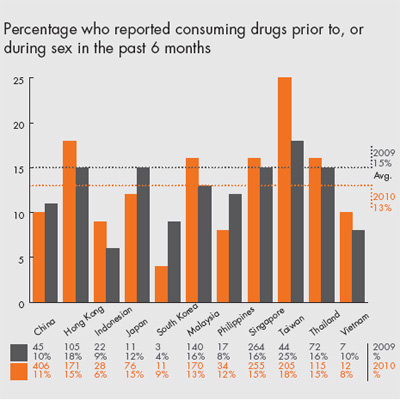
Limitations
1. The participants may not be representative of the Internet using MSM population
2. Marketing efforts in each country was not consistent and hence reach into each country's population was not equal. This means the demographic make up of respondents from each country is also not on par.
Discussion
Emerging trends
• Internet as primary means for men to meet other men for significant number of MSM who use the Internet
• Sex parties are becoming commonplace in most countries
• Recreational drugs, including methamphetamines are being used for sex
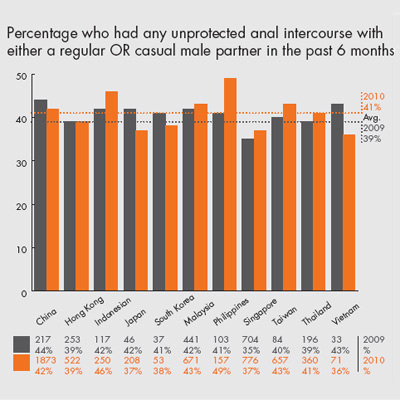
• Sex with regular partners have much lower rate of condomuse than with casual partners
Philippines is of particular concern and appears to have the preconditions for a future epidemic:
• Low condom use
• Low testing rates
• High prevalence amongst those who have been tested
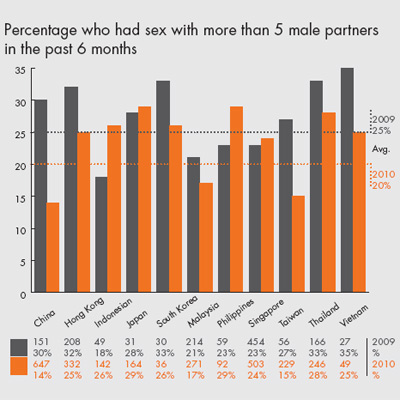
• Multiple sex partners
• Sex parties
Acknowledgements
This survey would not have been possible without the assistance and inputs from A Prof Nai-Ying Ko (Kaohsiung, Taiwan), Jane Koerner (Nagoya, Japan), FHI Vietnam, FHI Indonesia, Kosol (Rainbow Sky Association of Thailand), Philippe Girault, Jan van Wijngaarden, Brad Otto, Mandy Govender, Roy Ngerng, A Prof Roy Chan, and all our community coalition partners.
Dr Stuart Koe is founder and CEO of Fridae. He holds a Doctor of Pharmacy from the University of Minnesota, specialising in HIV therapy and is currently a Board member of Hong Kong’s Aids Concern (since 2006), a founding Trustee of Singapore’s Action for AIDS Endowment Fund (since 2003), and a long time AIDS activist, having also served on AfA’s Executive Committee for several terms (since 1998). He is also the Vice Chair of APCOM's first governing board, elected in June 2010.
