WARNING: Pictures below are very graphic.
One young man came in with penile discharge and the doctor diagnosed nongonoccocal urethritis. The young man shook his head and said it was impossible because he always used a condom. "But did you use a condom during oral sex?" the doctor asked.
Intro
Also known as: NGU, Chlamydia, UU, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Urethritis. Urethritis is any inflammation of your urethra (the tube that carries urine and semen through your penis). Most men notice a burning with urination and a discharge from the tip of their penis. There are over four million new cases of urethritis each year with one-third caused by gonorrhea and two-thirds caused by other infections.
What is it?
Nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) is any infection of your urethra caused by an organism other than gonorrhea and accounts for approximately two-thirds of the cases. Chlamydia trachomatis and Ureaplasma urealyticum are the most common organisms that cause this infection. Other bacteria can cause the infection, especially if you put foreign objects (and other toys) into your urethra. Men who require frequent catheterizations to remove their urine also frequently develop urethritis from other types of bacteria.
Diagnosis
Doctors diagnose the infection by examining your penile discharge under a microscope. If you have a noticeable discharge, your doctor will collect it on a cotton swab. If it's minimal, he/she will try to "milk" a little of it out of your urethra. When this fails, the last alternative (please don't squirm) is for your doctor to pass a tiny (emphasis on tiny) swab into your urethra. Don't worry; it doesn't go in very far.
When doctors examine the discharge produced by NGU under a microscope, they typically see many white blood cells without gonorrhea bacteria. Although different types of bacteria can cause NGU and might turn up as a positive culture, most cases of NGU are caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Ureaplasma urealyticum (UU). These organisms are exceedingly difficult to culture. If your doctor cultures your discharge (it takes several days to obtain a result) and a specific bacterium turns up, then your treatment will be tailored to kill that organism. Most often, however, no organism grows and your doctor suspects that you have NGU caused either by chlamydia or UU. Treatment will be tailored to kill these organisms. Alternatively, doctors can insert a small cotton swab into your urethra or dab it in a bit of your penile discharge (sound pretty?) and send it to the laboratory for DNA analysis. If chlamydial DNA is present in your discharge, then you know it caused your urethritis. This test is more reliable than a culture because the bacteria does not have to grow to identify its presence.
Symptoms
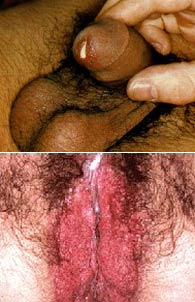
How is it acquired?
NGU is often a sexually transmitted infection. Like gonorrhea, it does not require penetration to spread between partners. Close physical contact may be enough. It can also be found in your throat and anus. Older men with prostate enlargement or men who require frequent catheterizations (passing a catheter down your urethra to your bladder to empty urine) are also at risk for developing urethritis. In these cases, many different types of bacteria can cause the infection. Men who pass foreign objects into their urethra are also at risk for infections. In addition to chlamydia (which can be found in a partner's throat), you can also develop urethritis from other bacteria that are normally present in a partner's mouth and then spread to your urethra during unprotected oral sex.
If untreated the infection can spread from your urethra to your epididymis and prostate. You can even spread it to other parts of your own body. Chlamydia is one of the most common STDs to infect your eye. And no, you didn't get it because some guy hit the target: your fingers spread it there.
How to treat it?
Most cases of NGU are caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and UU and doctors will often treat you for these infections even before the culture results return. (Don't forget that the culture is often unreliable because the organisms are so difficult to grow -- but your doctor treats you anyway). Many doctors will also treat you for gonorrhea at the same time -- again because it takes several days for the culture results to return -- days in which you can get sicker. The most common treatment for NGU is azithromycin (Zithromax) in a single one gram dose. Alternative treatments include tetracycline or doxycicline for one to two weeks.
Myths dispelled
Here are some facts to clear up some common misconceptions.
You don't get urethritis from toilet seats, unless perhaps someone else is sitting on your lap. Urethritis may not be sexually transmitted.
Prevention
A condom will prevent urethritis. You can catch urethritis when you insert your penis into someone's mouth or anus without a condom on.
Of particular concern to
NGU is one of the most common STDs.
Of particular concern to Men
NGU is very common in men. Symptoms may be mild and many men do not realize they have the infection. They can unwittingly spread it to partners. Chlamydia and UU can also infect your mouth and anus. If you pass foreign objects into your urethra you can cause an infection (urethritis). Men with penile piercings that pass through the urethra are also more likely to develop a urethritis which may not be sexually transmitted.
Of particular concern to Women
Urethritis is rare in women because your urethra is so short (you can figure out why). Chlamydia infections of the female genital tract are, however, very common.
Of particular concern to Older
As men age they develop prostate enlargement (BPH) and may have difficulty urinating. Catheters can cause urethritis.
Of particular concern to Immune Compromised
Urethritis is an STD. If you have this infection you are at increased risk for catching or transmitting HIV.
Incubation period
NGU has a longer and more variable incubation period than gonorrhea. Typically symptoms begin one to five weeks after the onset of infection.
Sex
Most cases of NGU are caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Ureaplasma urealyticum. A condom will protect you. You can catch urethritis from oral or anal sex, and other close contact. Penetration may not be necessary.











 Printable Version
Printable Version









Reader's Comments
Be the first to leave a comment on this page!
Please log in to use this feature.