This statement was issued on Oct 28, 2011 and co-signed by 53 organisations and 86 individual activists across Africa:
Statement Of African Social Justice Activists On The Threats Of The British Government To “Cut Aid” To African Countries That Violate The Rights Of LGBTI People In Africa
We, the undersigned African social justice activists, working to advance societies that affirm peoples’ differences, choice and agency throughout Africa, express the following concerns about the use of aid conditionality as an incentive for increasing the protection of the rights of LGBTI people on the continent.
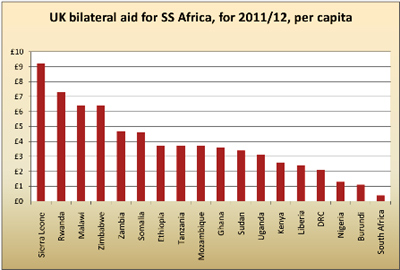
It was widely reported, earlier this month, that the British Government has threatened to cut aid to governments of “countries that persecute homosexuals” unless they stop punishing people in same-sex relationships. These threats follow similar decisions that have been taken by a number of other donor countries against countries such as Uganda and Malawi. While the intention may well be to protect the rights of LGBTI people on the continent, the decision to cut aid disregards the role of the LGBTI and broader social justice movement on the continent and creates the real risk of a serious backlash against LGBTI people.
A vibrant social justice movement within African civil society is working to ensure the visibility of – and enjoyment of rights by – LGBTI people. This movement is made up of people from all walks of life, both identifying and non-identifying as part of the LGBTI community. It has been working through a number of strategies to entrench LGBTI issues into broader civil society issues, to shift the same-sex sexuality discourse from the morality debate to a human rights debate, and to build relationships with governments for greater protection of LGBTI people. These objectives cannot be met when donor countries threaten to withhold aid.
The imposition of donor sanctions may be one way of seeking to improve the human rights situation in a country but does not, in and of itself, result in the improved protection of the rights of LGBTI people. Donor sanctions are by their nature coercive and reinforce the disproportionate power dynamics between donor countries and recipients. They are often based on assumptions about African sexualities and the needs of African LGBTI people. They disregard the agency of African civil society movements and political leadership. They also tend, as has been evidenced in Malawi, to exacerbate the environment of intolerance in which political leadership scapegoat LGBTI people for donor sanctions in an attempt to retain and reinforce national state sovereignty.
Further, the sanctions sustain the divide between the LGBTI and the broader civil society movement. In a context of general human rights violations, where women are almost as vulnerable as LGBTI people, or where health and food security are not guaranteed for anyone, singling out LGBTI issues emphasizes the idea that LGBTI rights are special rights and hierarchically more important than other rights. It also supports the commonly held notion that homosexuality is ‘unAfrican’ and a western-sponsored ‘idea’ and that countries like the UK will only act when ‘their interests’ have been threatened.
An effective response to the violations of the rights of LBGTI people has to be more nuanced than the mere imposition of donor sanctions. The history of colonialism and sexuality cannot be overlooked when seeking solutions to this issue. The colonial legacy of the British Empire in the form of laws that criminalize same-sex sex continues to serve as the legal foundation for the persecution of LGBTI people throughout the Commonwealth. In seeking solutions to the multi-faceted violations facing LGBTI people across Africa, old approaches and ways of engaging our continent have to be stopped. New ways of engaging that have the protection of human rights at their core have to recognize the importance of consulting the affected.
Furthermore, aid cuts also affect LGBTI people. Aid received from donor countries is often used to fund education, health and broader development. LGBTI people are part of the social fabric, and thus part of the population that benefit from the funding. A cut in aid will have an impact on everyone, and more so on the populations that are already vulnerable and whose access to health and other services are already limited, such as LGBTI people.
To adequately address the human rights of LGBTI people in Africa, the undersigned social justice activists call on the British government to:
· Review its decision to cut aid to countries that do not protect LGBTI rights
· Expand its aid to community based and lead LGBTI programmes aimed at fostering dialogue and tolerance.
· Support national and regional human rights mechanisms to ensure the inclusiveness of LGBTI issues in their protective and promotional mandates
· Support the entrenchment of LGBTI issues into broader social justice issues through the financing of community lead and nationally owned projects.
Read the ist of signatories — 53 organisations and 86 individual activists across Africa – here.
Credit: Daniel Berhane, http://danielberhane.wordpress.com
Scott Long, now a Visiting Fellow in the Human Rights Program of Harvard Law School and until recently Executive Director of the LGBT Rights Program at Human Rights Watch, commented on his blog, http://paper-bird.net:

There is some controversy over exactly what the British government actually said. Paul Canning of the chronically inaccurate blog LGBT Asylum News notes, accurately, that the story originated when the Daily Mail — a right-wing, anti-everything rag — spun a general Foreign Office statement on linking aid to human rights, and emphasized the LGBT angle. But Canning’s attempts to minimize the shift ignore the fact that David Cameron has prominently stressed the linkage in recent days. Just this weekend Cameron told the BBC:
“Britain is now one of the premier aid givers in the world. We want to see countries that receive our aid adhering to proper human rights, and that includes how people treat gay and lesbian people … British aid should have more strings attached, in terms of do you persecute people for their faith or their Christianity, or do you persecute people for their sexuality. We don’t think that’s acceptable.”
It’s hard not to conclude that this move is about domestic politics, not rights. The Daily Mail, piously endorsing the gay-rights cause (which it fought for years) used the emanations from the Foreign Office to further its anti-foreign-aid agenda — opining the government acted because “deeply rattled by the ferocious public opposition to its decision to increase overseas aid by more than one third while deep cuts are made in other areas.” (The UK has announced a 35% increase in overseas aid by 2013, in an effort to bring it up to the level of 0.7% of GDP recommended by a UN General Assembly resolution as long ago as 1970.) But there’s probably truth to this. Proclaiming loudly that he’s tying strings to aid gives Cameron some protection from the xenophobic fanatics on his own side of the political aisle. (Half of Tory MPs apparently want Britain to leave the EU; their attitude toward Malawi or Uganda can hardly be imagined.) If one of those strings is rainbow-colored, it also helps him with the gay vote. The Tories have been making a pitch for those ballots recently, with the PM publicly endorsing gay marriage. With the ruling coalition’s policies deeply unpopular, the Tories’ core support among foxhunters and Colonel Blimps needs a rejuvenating jolt from a new constituency.
In other words, as the activists’ letter says, the UK’s internal politics are dictating the lives and determining the safety of LGBT communities in other countries. An Indian blogger comments:
There is another more urgent and specific problem with the UK government policy – and that is the manner in which it denies the possibility that there might be local movements, dialogues and activisms around sexuality and homophobia. … At one level it places the concern for sexuality rights outside the given country, and at another, it disavows the significance and strategies of local activists and movements that are engaged in the project of actualising citizenship.
While the rise of sexuality on the development and rights agenda, is a welcome development, to be truly progressive western forces might do better by supporting Queer movements in the global south, learning from them, and recognising the specificities of Queer struggles.











 打印版本
打印版本










读者回应
Malawi and other countries who don't agree with the British conditions can look for funds elsewhere. Maybe their neighboring African country who promote the totally outrageous contention that all gays are pedophiles and "... ita da poo poo" can lend them a hand.
It's about time countries start to look more closely at the abhorrent ways the recipient countries treat their peoples. One day even Australia will open it's eyes before it's purse.
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/politics/7747998/Did-Britain-really-need-to-give-millions-tothe-wealthy-state-of-Singapore.html
then we won't be able to 'ita da poo poo' anymore.
damn ...
;-)
Speaking of Karma, here's one very interesting article about Pope Benedict's anti-gay speech in Madrid interrupted by...VIOLENT THUNDERSTORM. “Powerful winds and sheets of rain struck at a vast air base, whipping off his skullcap, shaking the stage and knocking over at least one tent.” http://unicornbooty.com/blog/2011/08/22/pope-gives-anti-gay-speech-angry-god-blows-his-hat-stage-down/
Hmmm...it seems his God must be more than a tad pissed with him lol
It is agreed that public opinion can not be changed overnight and as a first step step banning public displays of "unacceptable behavior" would be at least an "improvement"
请先登入再使用此功能。