This survey was conducted by MSM HIV/STI Prevention Programme under Action for AIDS (Singapore) from Nov 2002 to Feb 2003 among men who have sex with men (MSM) in Singapore to investigate sexual and HIV-related knowledge, attitudes, and behaviour, and to develop appropriate intervention measures as needed. 1,291 responses were collected, excluding four which had to be discarded.
Survey Venue and Language
The responses were collected through the survey website (76.3%) as well as from 3 gay saunas (12.1%), AfA's HIV Anonymous Testing Centre (6.3%), 3 gay clubs/bars (5.0%), and from the DSC Clinic (0.3%), a clinic handling sexually-transmitted infections (STI). Most respondents (97.9%) completed the English questionnaire, the remaining 2.1% filled out the Chinese one.
The Respondents
Nationality: 74.1% Singaporean, 12.4% Malaysian, 13.5% other nationalities
Age: 13.5% below 21, 14.1% in the 22-24 age group, 48.6% in the 25-34 age group, 18.8% in the 35-44 age group, 4.9% aged 45 and above
Ethnicity: 76.2% Chinese, 7.3% Malay, 3.5% Indian, 3.1% Eurasian, 6.0% Caucasian, 3.8% others
Marital Status: 95.6% single, 2.7% married, 1.0% divorced, 0.6% separated, 0.1 % widowed
Education: 0.9% no formal qualification/primary education, 12.4% secondary, 3.8% ITE/NTC, 10.8% JC/Pre-U Centre, 19.7% polytechnic, 37.2% university degree, 15.1% postgraduate degree
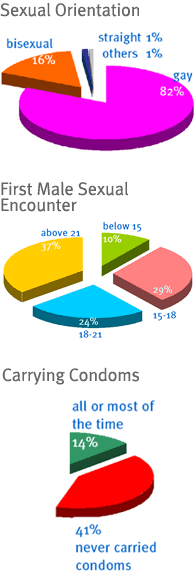
81.7% identified as 'gay', 16.3% as 'bisexual', 1.3% as 'straight', and 0.7% identified their sexual orientation in other ways. Younger respondents and those with lower educational qualifications were less likely to identify as 'gay'.
First Sexual Encounter with Another Male
Most respondents started having oral/anal sex with other males from 15 to 18 years of age (29.1%) or from 19 to 21years of age (24.4%). 10.3% had their first sexual encounters below the age of 15 and were also more likely to have had unprotected anal sex when they first started having sex. Others more likely to have had unprotected anal sex at their first sexual encounter were those with only secondary or ITE/NTC education. In general, however, oral sex was most common at the first sexual encounter.
Ways of Meeting Sexual Partners
The internet was the most common way of meeting sexual partners (60.6%), though this result could have been influenced by the large number of results collected online. 47.8% met sexual partners at gay saunas, 30.3% at gay clubs/bars, and 28.1% through friends and social events. The likelihood of meeting sexual partners through the internet decreased with age while that of meeting sexual partners at gay saunas increased with age. Caucasians were more likely to have met their sexual partners in gay clubs/bars.
Carrying Condoms
The likelihood of respondents carrying condoms increased with age but only 13.5% carried condoms all or most of the time. 41.2% never carried condoms with them. Very few respondents who carried condoms all or most of the time (naturally) had had unprotected anal sex. Many Caucasians fell into this category.
Relationship Status
Almost equal proportions of respondents had a boyfriend when they filled out the questionnaire (39.6%) or were single but had had one before (39.8%). 20.6% had never had a boyfriend before. Many with lower educational qualifications fell into the third category. Of those with boyfriends at the time of the survey, a high proportion had had only one sexual partner in the 3 months before completing the survey form.
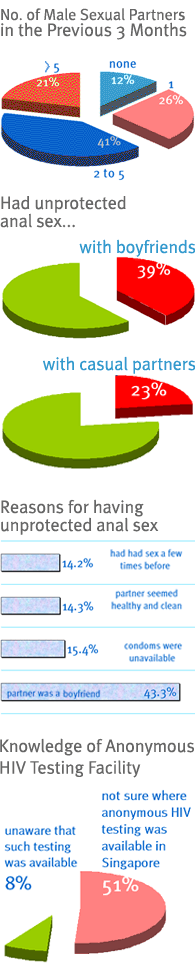
Most respondents had had two to five partners (41.4%) within this time frame, 25.5% had had one partner, 20.9% more than five partners, and 12.2% no sexual partners. The number of sexual partners tended to increase with age. Caucasians and those who had never had a boyfriend before were more likely to have had more than five sexual partners.
Sex with Boyfriends vs. Sex with Casual Partners
Oral sex was predictably the most common sexual practice with both boyfriends and casual partners.
Respondents were more likely to have had unprotected rather than protected anal sex with boyfriends. With casual partners, respondents were more likely to have had protected rather than unprotected anal sex. 39.3% had had unprotected anal sex with boyfriends, 22.9% had had unprotected anal sex with casual partners.
Unprotected anal sex with casual partners was more common among respondents with ITE/NTC education, those who met their sexual partners through the internet, and those who had sex in hotel rooms, cruising areas, cars, public places, camps and hostels. Fewer respondents from the gay saunas and gay clubs/bars reported having had unprotected anal sex.
Reasons for Unprotected Anal Sex
The most common reason was that the sexual partner was a boyfriend (43.3%). Other common reasons were that condoms were unavailable (15.4%), the partner seemed healthy and clean (14.3%), and they had had sex a few times before (14.2%).
Venue for Sex
Home was the most common venue for sex (85.2%), followed by hotel rooms (52.2%), gay saunas (45.7%), cars and public places (22.8%), and cruising areas (21.3%). The likelihood of having sex at saunas increased with age.
Sex while 'High' on Alcohol/Recreational Drugs
21.3% of the respondents had had sex while drunk, 4.0% while 'high' on drugs, and 8.0% while under the influence of both alcohol and drugs. Those in the final category were more likely to have unprotected anal sex. Many Caucasians reported having sex while drunk and/or 'high'.
Choice of Lubricant
The most common lubricants used were the safest ones, water-based lubricants (76.5%). However, unsafe lubricants such as saliva (20.3%), creams, lotions and oils (15.5%), and soap and shower gels (5.3%) were significantly popular, too. Caucasians were more likely to use water-based lubricants and NOT to use oil-based ones.
Sexually-Transmitted Infections (STI)
81.0% responded that they had never been diagnosed with an STI. The most common STI mentioned were gonorrhoea (7.2%), genital/anal warts (5.0%), non-gonococcal urethritis (2.9%), herpes (2.6%), hepatitis B (2.1%), and syphilis (2.0%). The likelihood of having had an STI increased with age.
HIV Testing History
1.6% had tested positive. 40.4% of the respondents had never been for an HIV test. Of these, many were unsure about the availability of anonymous HIV testing in Singapore. The likelihood of never having tested decreased with age. Many Malay respondents had never tested before.
Knowledge of Anonymous HIV Testing Facility
More than half the respondents (51.1%) were not sure where anonymous HIV testing was available in Singapore, while another 8.4% were unaware that such testing was available here. Respondents below 21 years of age were more likely to be unsure about the availability of anonymous HIV testing in Singapore. Interestingly, many Malays named the correct venue for anonymous HIV testing.
Discussing HIV Status with Partners
47.2% had never asked any partner about their HIV status while 48.9% had never disclosed their HIV status to any partner.
Perceptions of Risk
While 93.1% correctly identified having unprotected receptive (being the 'bottom') anal sex as high risk, only 78.5% regarded unprotected insertive (being the 'top') anal sex as high sex. This might lead to a false sense of security for 'tops'. In addition, a high proportion of those who considered unprotected receptive anal sex as low risk had had such sex with casual partners.
Some low risk activities such as protected anal sex, receiving oral sex, and rimming were considered medium risk by a significant number of respondents (15.7% to 25.7%).
Situations such as touching HIV-positive people, sharing food, drinks and eating utensils with them, and being bitten by mosquitoes were assessed as being no risk situations by only 70.2% to 75.2% of the respondents. Attributing risk to these situations is likely to bring about unnecessary fear of and discrimination against HIV-positive people.
Unprotected Sex with Women
79.1% of the respondents had never had sex with women, while 12.0% had had unprotected sex with women.
Areas of Concern
The survey has helped us identify the following issues:
- starting to have sex at a younger age, which is likely to involve unprotected anal sex
not carrying condoms.
- use of non-water-based lubricants with condoms.
- high levels of unprotected anal sex, especially with boyfriends, casual partners, partners who seemed healthy, and regular sex partners.
- having sex while under the influence of alcohol and/or drugs.
- perception that being a 'top' is much less risky.
- low levels of HIV testing and ignorance about anonymous HIV testing being available.
- inaccurate risk assessments, including of no risk situations.
- significant unprotected sex with women.
The groups most at risk seemed to be the younger MSM and those with lower educational qualifications.
The findings of the survey are being used to develop new sexual health material and to plan other intervention measures.











 列印版本
列印版本
















讀者回應
搶先發表第一個回應吧!
請先登入再使用此功能。